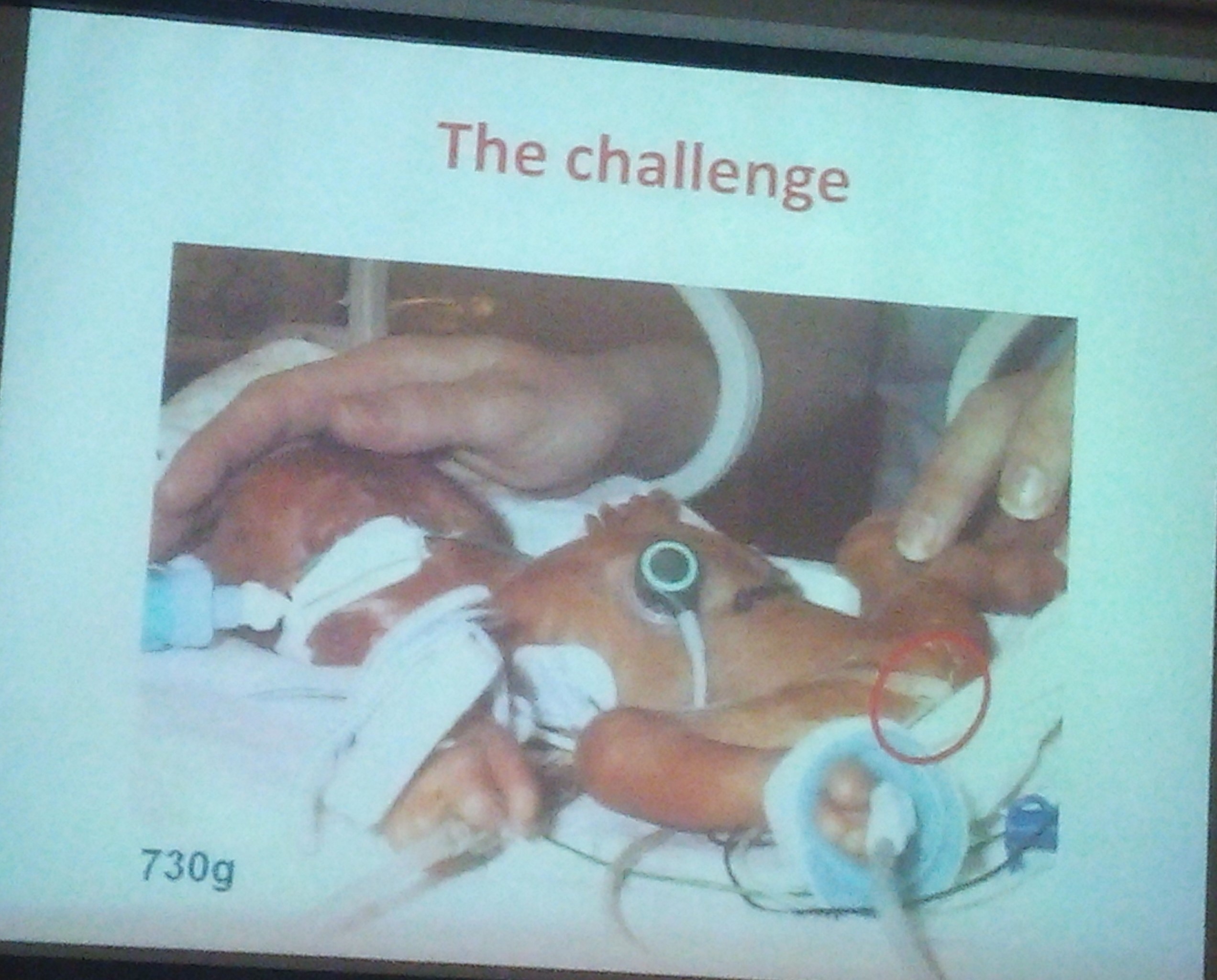
Just saw a neonate whose mother took Nimesulide whole of her pregnancy for pain abdomen, and now the child is in renal failure. It is a difficult task counselling these parents with a neonate with renal failure.
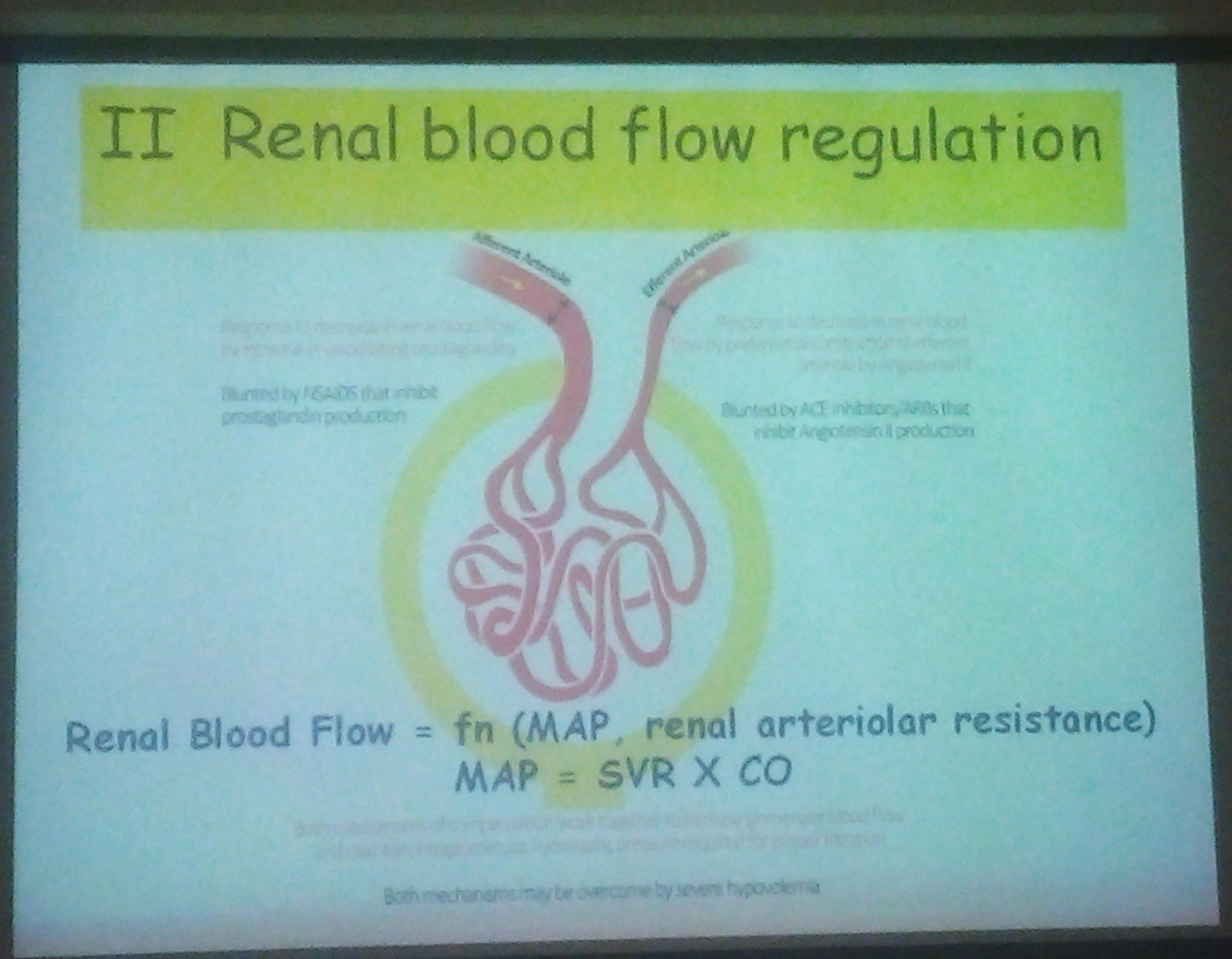
Renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD) is characterized by absent or poorly developed proximal convoluted tubules.
The glomeruli appear numerous because of the absent proximal tubules in the cortex. Tubules are dilated, and the interstitium is expanded. RTD has been reported to occur as an inherited genetic defect. It has been recognized as a characteristic feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor foetopathy. It has also been reported sporadically in association with exposure to other drugs, notably the non-selective, non-steroidal, antiinflammatory drugs
Image Source
Renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD) is characterized by absent or poorly developed proximal convoluted tubules.
The glomeruli appear numerous because of the absent proximal tubules in the cortex. Tubules are dilated, and the interstitium is expanded. RTD has been reported to occur as an inherited genetic defect. It has been recognized as a characteristic feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor foetopathy. It has also been reported sporadically in association with exposure to other drugs, notably the non-selective, non-steroidal, antiinflammatory drugs
Image Source