Curofy- India's largest community of verified doctors covered the CME-International Neonatal and Pediatric Nephrology Training Workshop live. This post was first published on the Curofy app.
Glomerular function:
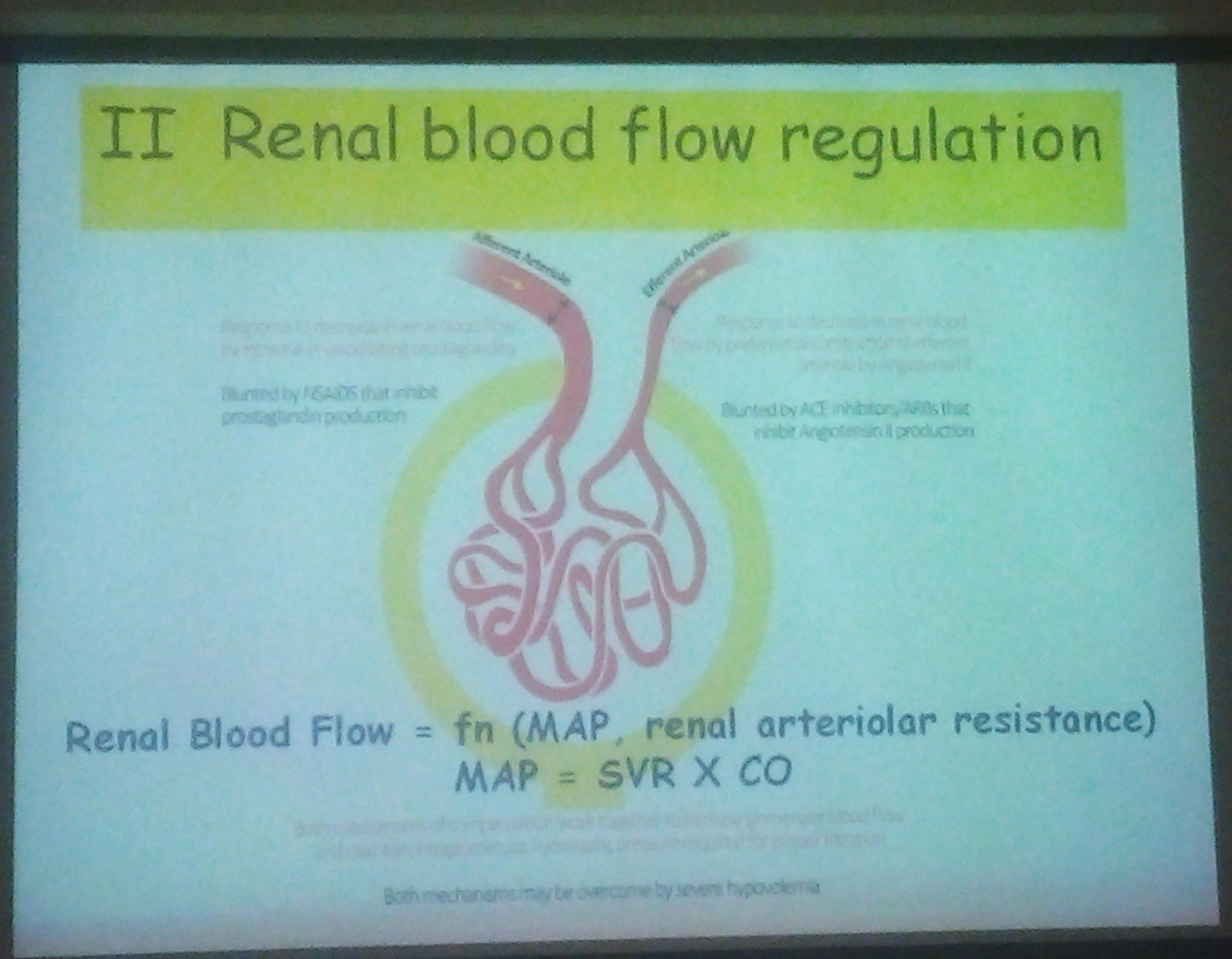
Kidney receives 15% of CO
Low systemic blood pressure
Increased vascular resistance
Renal blood flow more to inner cortex and medulla
GFR is 10-30 ml/min/1.73m2
Limited adaptive features to stress, sepsis, anorexia and exposure to nephrotoxic drugs are challenges in assessing renal function
Autoregulation:
Range of autoregulation set to lower perfusion pressure
Susceptible to Hypovolemic insult
Tubular function:
Total body water 75% of the weight
Shift of ECF into cells
Physiologic weight loss 10-15%
Low urine concentrating capacity
Dilution mechanism better than conc. capacity
Prone to dehydration
It maybe non oligouric despite poor renal function
Sodium balance:
Hyponatremia in preterms and rapidly growing LBW babies
Potassium levels of 6-6.5 is considered acceptable in term and preterm neonates
Acid base balance:
Suboptimal acid excretion
Lower serum bicarbonate levels are acceptable in preterm and term neonates
Disease states and drugs can accentuates metabolic acidisis.
Why did AK failure become AK injury, it should be AK dysfunction
Deficiency of AK*
Reduced GFR
Reduced urine output
Pre-renal causes:
Hypovolaemia
Non osmotic release of ADH
Renin/endocrine
Renin/paracrine
-Furosemide
does not lead to damage if reverses
Management:
Deal with reversible components
Improve renal perfusion
Sepsis
Surgery
Multiple organ failure
Furosemide if indicated
Obsessional fluid care
Blood results for fine tuning
When to dialyze?
Fluid is the key. If oligouric keep using conservative management until biochemistry is life threatening
Neonatal Renal Physiology
Dr Saroj patnaik
Dr Saroj patnaik
Glomerular function:
Kidney receives 15% of CO
Low systemic blood pressure
Increased vascular resistance
Renal blood flow more to inner cortex and medulla
GFR is 10-30 ml/min/1.73m2
Limited adaptive features to stress, sepsis, anorexia and exposure to nephrotoxic drugs are challenges in assessing renal function
Autoregulation:
Range of autoregulation set to lower perfusion pressure
Susceptible to Hypovolemic insult
Tubular function:
Total body water 75% of the weight
Shift of ECF into cells
Physiologic weight loss 10-15%
Low urine concentrating capacity
Dilution mechanism better than conc. capacity
Prone to dehydration
It maybe non oligouric despite poor renal function
Sodium balance:
Hyponatremia in preterms and rapidly growing LBW babies
Potassium levels of 6-6.5 is considered acceptable in term and preterm neonates
Acid base balance:
Suboptimal acid excretion
Lower serum bicarbonate levels are acceptable in preterm and term neonates
Disease states and drugs can accentuates metabolic acidisis.
Neonatal AKI
Dr Malcolm Coulthard
Dr Malcolm Coulthard
Why did AK failure become AK injury, it should be AK dysfunction
Deficiency of AK*
Reduced GFR
Reduced urine output
Pre-renal causes:
Hypovolaemia
Non osmotic release of ADH
Renin/endocrine
Renin/paracrine
-Furosemide
does not lead to damage if reverses
Management:
Deal with reversible components
Improve renal perfusion
Sepsis
Surgery
Multiple organ failure
Furosemide if indicated
Obsessional fluid care
Blood results for fine tuning
When to dialyze?
Fluid is the key. If oligouric keep using conservative management until biochemistry is life threatening
No comments:
Post a Comment