Curofy- India's largest community of verified doctors covered the CME-International Neonatal and Pediatric Nephrology Training Workshop live. This post was first published on the Curofy app.
Basics of RRT
Speaker: Dr. Pranaw Jha
Speaker: Dr. Pranaw Jha
Dialysis process whereby soluble composition of a solution A is altered by exposing to solution B across a semipermeable membrane
-Need 2 solution- blood & dialysate
-Semi permeable membrane
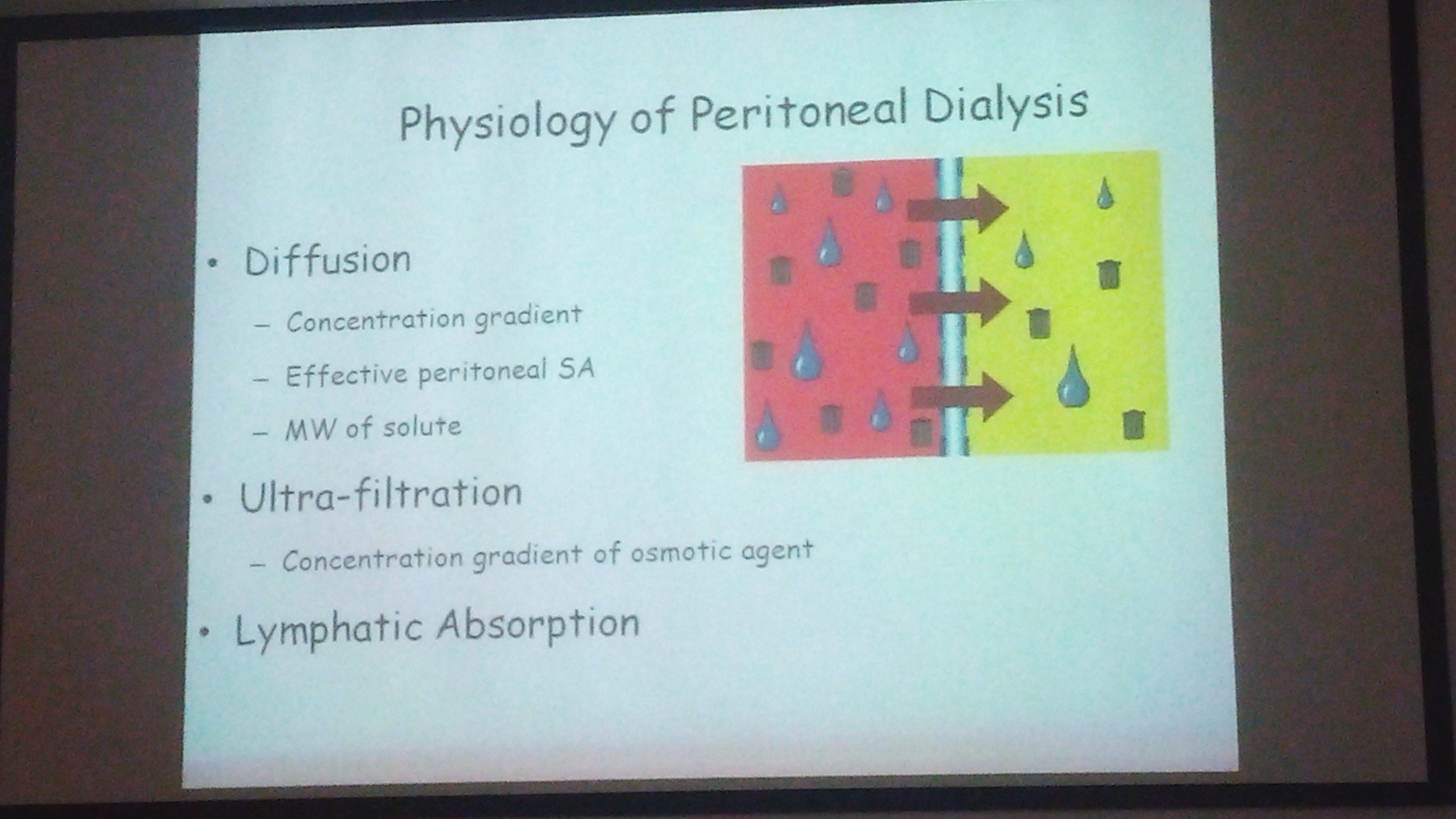
Transport mechanisms:
Diffusion
Convection
Adsorption
Osmosis
Diffusion:
results in random molecular motion
inversly proportional to solute ssite
Convection:
Ultrafilteration
water driven across semipermeable membrane by hydrostatic/ osmotic force
solvent swept along with it, close to concentrated gradient- solvent drag
Convective methods:
Hemofilterationlarge amount of ultrafilteration coupled with replacement fluid infusion.
Hemodiafilteration: combined HD & HF
Dialysis Modality
Dr. Siddhartha Sethi
Dr. Siddhartha Sethi
Choice of modality
Peritoneal dialysis
intermittent hemodialysis
CRRT
PD is declining in the west, since expertise is increasing. CRRT is used
Modality of choice in India
less expertise in India
not insured in India
expensive
indication of CRRT
prevention of fluid overload
Acute peritoneal dialysis:
indication: Refractory volume overload
refract hyperkalemia
refract metabolic disease
uremia complication
dysnatemias in AKI
Apparatus:
PD catheter
three way connector
IV sets
PD fluid bags
Drain bag
Catheter:
Stiff catheter
two cuff tenckhoff's catheter
Cook's catheter
tenckhofs single cuff
soft thermal
Bicarbonate dialysis
Severe lactic acidosis or hepatic failure
asepsis required
1 hr exchange time
Ultra filtration
Not more than 5-10% weight loss should be targeted
Session length: Stiff catheter are 48-72 hr affair
anuria, hypercatabolism, nutritional support
Additives:
heparin, potassium, insulin
Disadvantage:
Slower concentration
lower URA clearance
lower ultra filtration
risks of peritonitis
Automated PD:
warm fluids, keeps track, less infection
Prescribing HD & Mathematics
Dr. Rupesh Raina
Dr. Rupesh Raina
Dialysis cannot clear solutes not present in intravascular space.
Diffusion:
Factors:
Conc. gradient(dC)
surface area(A)
diffusivity(KO)
sum of resistance(dx/KO)
concurrent flow
time
J=KOA x dC/dx
Solutes:
Low molecular weight- uo to 300 daltons
middle molecular weight- 300- 2000 daltons
large molecular weight- 5000- 1200 daltons
serum albumin-69 366 D
Hollow fiber dialyser;
Thousands of hollow capillary sizes fibers fixed in a polyurethane capsules.
blood flows through fibers, dialysate flows around fibers
Clearance: volume of blood cleared of solute per unit time.
( Refer pic)
KoA
Product of the overall mass transfer co efficient for a given solute x dialyser surface area
Ultrafilteration co efficient: ( KUf)
Volume of fluid transferred across the membrane per mmHg of pressure gradient
Low KUf denotes low permeability and low flux
high KUf denotes near complete permeability
High flux of dialyzers: KUf> 14ml/min/mmhg
Urea kinetic modeling:
Process to determine the amount of dialysis actually given
uses mathematical equation
( refer urea soup pic)
KT/V( Urea)
represnts fractional ura clearance
K= dialyzer clearance
T= time
V= volume of urea distribution
-0.5= uremic, death
-0.7= EEg abnormal
-1.0= short trm
-1.2-1.4= long term
->1.4= better outcome
Initial hemodynamic prescription concepts; Aim to prescribe a dose of dialysis to effect a desired result
Tubing: < 10 kg- neonatal tubing
10-20 kg- pediatric tubing
>20 kg adult tubing
SLED & CRRT
Dr. Timothy Buchman
Dr. Timothy Buchman
Continuous form of renal replacement therapy that allows for hemodynamic stability
SLED: Slow Low Efficiency Dialysis
Pediatric data for CRRT: optimal use in situation of hemodynamic compromise, Hypermetabolic state, sepsis
45% survival
Pediatric data SLED:
Heparin Anticoagulation
14 children in 16 sessions. less than 8 hours.
cheaper than CRRT
Advantages of CRRT:
Continuous in nature making decision making of medication, dosage and nutrition delivery easier.
Hemodynamically stable
Disadvantages, of CRRT:
greater need of utilization of resources
High pharmacy costs
Adv. of SLED
less resource utilization
less expensive
hemodialysis in morning and nocturnal SLED at night
Disadvantages of SLED
may cause hemodynamic compromise
intermittent
risk of over dialysis due to minimal dialysate flow of 6 ltrs per hour



No comments:
Post a Comment